Describe the Structure and Function of the Connective Tissue Matrix
Our blood brings oxygen and nutrients all over the body and transports waste products to the kidneys and liver. Together the ground substance and fibers make up the extracellular matrix.

The Following Flow Chart Depicts The Different Types Of Connective Tissue And How They A Basic Anatomy And Physiology Tissue Types Human Anatomy And Physiology
Cartilage is a soft elastic and flexible connective tissue that protects the bone from rubbing against each other.

. One or more than one type of fibre and materials like calcium carbonate may remain present in matrix Figure. Soft and specialized connective tis. The unique and complex structure of articular cartilage makes.
Fibers are densely packed and organized in parallel to create a strong tissue capable of withstanding the pull of muscle and bone in movement. In the dense regular connective tissue the orientation of fibres are regular. - protects and supports the body and its organs.
It consists of cells fibers ground substances. Connective tissue can bind support protect insulate store reserve fuel. Tissues of the human body can be classified under 4 major sub-types.
- cells separated from each other by extracellular matrix. As may be obvious from its name one of the major functions of connective tissue is to connect tissues and organs. Soft and specialized connective tissue.
Their main function is to support and transmit mechanical forces. What is the function and location of reticular tissue forms framework for liver spleen lymph nodes and bone marrow what are the three types of dense connective tissue. They are somewhat less flexible than loose connective tissue.
Connective tissue is classified into two subtypes. Compare and contrast epithelial tissues epithelial membranes and synovial membranes. Connective tissue may transform into skeletal tissue fibrous tissue and.
Connective tissue functions. CONNECTIVE TISSUE PROPERTIES. The proportions of these components vary.
Generally connective tissues are made up of cells and the extracellular matrix that they produce. How can so many structurally-different types of tissues can all be connective tissues. Major functions of connective tissue include.
Cells fibers and ground substance. Epithelium nervous and muscle tissue. Connective tissue is the most widely distributed of the primary tissues.
Describe the components of a connective tissue matrix chemicals and fibers. The pericellular matrix is a thin layer adjacent to the cell membrane completely surrounding the chondrocyte. Tap card to see definition.
Dense regular connective tissue makes up tendons and ligaments. 4 rows The second major component of the ECM is the PGs a diverse group of soluble macromolecules that. Cartilage is smooth and lubricated to provide for easy pain-free movement.
A few distinct cell types and densely packed fibers in a matrix characterize these tissues. It contains mainly proteoglycans as well as glycoproteins and other non-collagenous proteins. The collagen fibres are present between the parallel running bundles of.
Connective tissue function is structural metabolic and protective. Connective tissue has three main components. Compare and contrast the structure and function of hyaline cartilage and compact bone.
The extracellular fibers of the matrix are secreted by the connective tissue cells and are responsible for the functional properties of the tissue. Epithelial nervous muscle and connective Delforge 2002. Connective tissue is classified into two subtypes.
All connective tissue is derived from mesoderm. 1 binding and supporting 2 protecting 3 insulating 4 storing reserve fuel and 5 transporting substances within the body. One of the important functions of the connective-tissue cells is to maintain conditions in the extracellular spaces that favour this exchange.
The functions of various connective tissues are to bind cells together to form and organize tissues organs and systems and to provide a mechanical link between musculoskeletal junctions and the articulations of joints. - various types of connective tissue binds together stores energy as fat and help provide immunity. The high number of.
The pericellular matrix region may play a functional role to initiate signal transduction within cartilage with load bearing. Connective tissue is classified into two subtypes which are soft and specialized connective tissue. Its primary cell types are chondrocytes.
After following this topic you should know about the basic structure and function of connective tissue and its components cells fibres ground substance. Bone tissue osseous tissue is extremely rigid and absorbs energy. Soft connective tissue cartilage bone.
Cartilage is an important structural component of the body. On the basis of the arrangement of collagen fibres they are divided into two types. The ground substance fibers make up the extracellular matrix.
General structure of connective tissue. Dense irregular connective tissue also contains abundant fibers but lacks the directionality of dense regular connective tissue fibers. The matrix is responsible for the specific structure and function of the tissues as the matrix of bone is rigid and inflexible but that of cartilage is firm but pliable.
Together the ground substance and fibers make up the extracellular matrix. It fills the spaces between organs and tissues and provides them with structural and metabolic support. Unlike epithelial tissue which is composed of cells closely packed with little or no extracellular space in between connective tissue cells are dispersed in a matrixThe matrix usually includes a large amount of extracellular material produced by the connective tissue.
Connective tissue is found deep and in-between the other three types of tissue. Components of connective tissue. As may be obvious from its name one of the major.
Connective Tissue is one of the four basic tissue types. All forms of connective tissue are composed of 1 extracellular fibres 2 an amorphous matrix called ground substance and 3 stationary and migrating cells. Connective tissue connects muscle with muscle and bone with bone.
Connective tissue bind cells other forms of tissues and organs in a way which provides mechanical support strength. April 16 2018 in Blog Immune Lymphatic Muscular Skeletal.
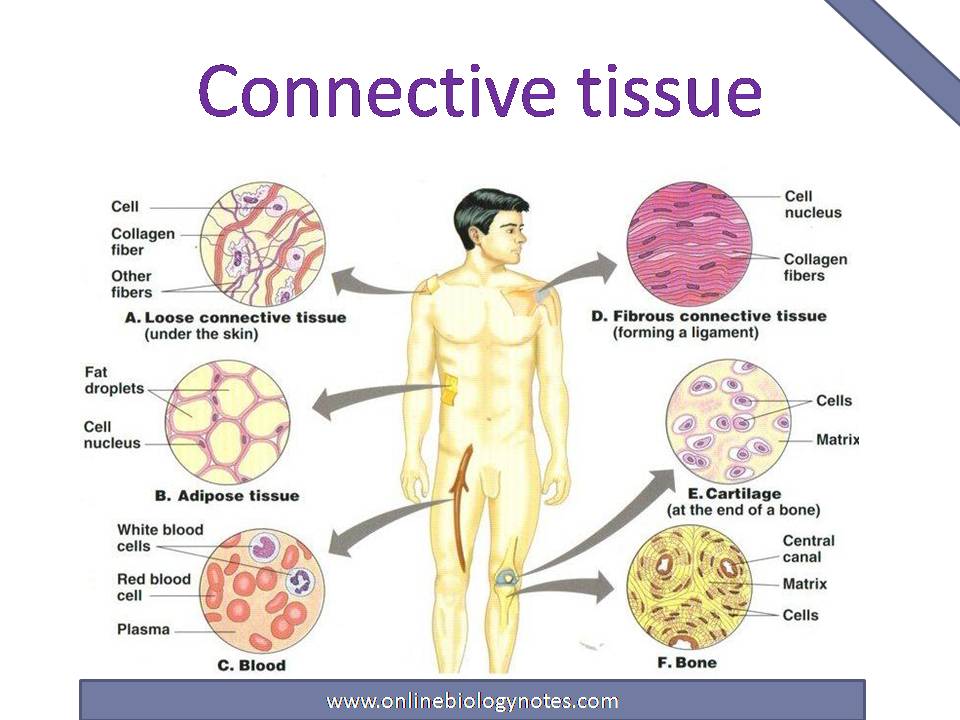
Connective Tissue Characteristics Functions And Types Online Biology Notes

The Cells And Fibers Of Connective Tissue Proper Anatomy And Physiology Textbook Human Anatomy And Physiology Pharmacology Nursing

Difference Between Epithelial And Connective Tissue Comparison Summary Tissue Biology Basic Anatomy And Physiology Anatomy And Physiology

Cell 6 Cells Tissues Connective Tissue Cells In Human Body Tissue Biology Anatomy And Physiology Human Tissue
No comments for "Describe the Structure and Function of the Connective Tissue Matrix"
Post a Comment